This conversion is done for import items from any source into Oracle Inventory and Oracle Engineering.
Description:
When you import items through the Item Interface, you create new items in your item master organization or assign existing items to additional organizations. You can specify values for all the item attributes, or you can specify just a few attributes and let the remainder default or remain null. Here we are importing items with template.
Interface Table:
- The interface table for Item Import is MTL_SYSTEM_ITEMS_INTERFACE and it contains every column in the Inventory item master table, MTL_SYSTEM_ITEMS.
- The columns in the item interface correspond directly to those in the item master table.
- Except for ITEM_NUMBER or SEGMENTn columns, ORGANIZATION_CODE or ORGANIZATION_ID, DESCRIPTION, PROCESS_FLAG, and TRANSACTION_TYPE, all other columns are optional, either because they have defaults that can be derived, or because the corresponding attributes are optional and may be left null.
- If you are importing revision details for your new items, you can use the MTL_ITEM_REVISIONS_INTERFACE table. This table is used only for revision information, and is not mandatory.
Required Data:
ITEM_NUMBER or SEGMENTn columns
Every row in the item interface table must identify the item and organization. To identify the item when importing it, you may specify either the ITEM_NUMBER or SEGMENTn columns—the Item Interface generates the INVENTORY_ITEM_ID for you.
ORGANIZATION_ID or ORGANIZATION_CODE
You need to specify either the ORGANIZATION_ID or ORGANIZATION_CODE that identifies the organization.
DESCRIPTION
When you import a new item, you are also required to specify the DESCRIPTION.
TRANSACTION_TYPE & PROCESS_FLAG
There are two other columns the Item Interface uses to manage processing. They are TRANSACTION_TYPE, which tells the Item Interface how to handle the row, and PROCESS_FLAG, which indicates the current status of the row.
Always set the TRANSACTION_TYPE column to CREATE, to create an item record (true when both importing a new item and assigning an already existing item to another organization). This is the only value currently supported by the Item Interface. The Item Interface uses the PROCESS_FLAG to indicate whether processing of the row succeeded or failed. When a row is ready to be processed, give the PROCESS_FLAG a value of 1 (Pending), so that the Item Interface can pick up the row and process it into the production tables.
Meaning of PROCESS_FLAG Values:
| Code |
Code Meaning |
| 1 |
Pending |
| 2 |
Assign complete |
| 3 |
Assign/validation failed |
| 4 |
Validation succeeded; import failed |
| 5 |
Import in process |
| 7 |
Import succeeded |
Note:
When more than one of these columns has been entered and they conflict, ITEM_NUMBER overrides SEGMENTn and ORGANIZATION_ID overrides ORGANIZATION_CODE. It is strongly recommended that you use SEGMENT column instead of ITEM_NUMBER.
For performance purpose, it is advised to batch set of records using set_process_id column and then run import program for that set_process_id. The item import (IOI) program can be run in parallel if separate set_process_ids are passed while submitting.
Derived Data:
Many columns have defaults that the Item Interface uses when you leave that column null in the item interface table. Please refer Oracle Manufacturing APIs and Open Interfaces Manual for more details.
Validations:
1] Validation for organization code (standard table: ORG_ORGANIZATION_DEFINITIONS)
2] Validation for Item_number (standard table: mtl_system_items_b)
3] Validation for Description
4] Validation for Primary Unit of Measure (standard table: MTL_UNITS_OF_MEASURE)
5] Validation for Template Name (standard table: mtl_item_templates)
6] Validation for Item Type (standard table: FND_COMMON_LOOKUPS)
7] Validation for ENCUMBRANCE_ACCOUNT (standard table: gl_code_combinations)
8] Validation for EXPENSE_ACCOUNT (standard table: gl_code_combinations)
Note: You can add more validation as per your business requirement.
Record Insertion:
Through your custom program you can insert the below columns in the interface table. Again the list is a sample one; you can add additional columns as your business requirement.
Columns inserted:
- ORGANIZATION_ID –>Taken from ORG_ORGANIZATION_DEFINITIONS table
- ORGANIZATION_CODE –>Taken from Staging table
- LAST_UPDATE_DATE –>sysdate
- LAST_UPDATED_BY –>fnd_global.user_id
- CREATION_DATE –>sysdate
- CREATED_BY –>fnd_global.user_id
- LAST_UPDATE_LOGIN –>fnd_global.login_id
- DESCRIPTION –>Taken from Staging table
- SEGMENT1 –>Taken from Staging table
- PRIMARY_UOM_CODE –>Taken from Staging table
- PRIMARY_UNIT_OF_MEASURE –>Taken from MTL_UNITS_OF_MEASURE
- ITEM_TYPE –>NULL
- TEMPLATE_NAME –>Taken from Staging table
- TEMPLATE_ID –>Taken from mtl_item_templates
- MIN_MINMAX_QUANTITY –>Taken from Staging table
- MAX_MINMAX_QUANTITY –>Taken from Staging table
- LIST_PRICE_PER_UNIT –>Taken from Staging table
- ITEM_CATALOG_GROUP_ID –>Taken from Staging table
- SET_PROCESS_ID –>1
- PROCESS_FLAG –>1
- TRANSACTION_TYPE –>‘CREATE’
Standard Concurrent Program:
After you insert valid data into Interface table, you can go to Items > Import > Import Items and run the standard concurrent program. Here is the parameter form.

1] All Organizations:
- Yes: Run the interface for all organization codes in the item interface table.
- No: Run the interface only for the organization you are currently in. Item interface rows for organizations other than your current organization are ignored.
2] Validate Items:
- Yes: Validate all items and their data residing in the interface table that have not yet been validated. If items are not validated, they will not be processed into Oracle Inventory.
- No: Do not validate items in the interface table.
3] Process Items:
- Yes: All qualifying items in the interface table are inserted into Oracle Inventory.
- No: Do not insert items into Oracle Inventory.
4] Delete Processed Rows:
- Yes: Delete successfully processed items from the item interface tables.
- No: Leave all rows in the item interface tables.
5] Process Set:
Enter a number for the set id for the set of rows you want to process. The program picks up the rows marked with that id in the SET_PROCESS_ID column. If you leave this field blank, all rows are picked up for processing regardless of the SET_PROCESS_ID column value.
Working with failed interface rows:
If a row fails validation, the Item Interface sets the PROCESS_FLAG to 3 (Assign/validation failed) and inserts a row in the interface errors table, MTL_INTERFACE_ERRORS. To identify the error message for the failed row, the program automatically populates the TRANSACTION_ID column in this table with the TRANSACTION_ID value from the corresponding item interface table.
The UNIQUE_ID column in MTL_INTERFACE_ERRORS is populated from the sequence MTL_SYSTEM_ITEMS_INTERFACE_S. Thus, for a given row, the sequence of errors can be determined by examining UNIQUE_ID for a given TRANSACTION_ID.
You should resolve errors in the sequence that they were found by the interface, that is, in increasing order of UNIQUE_ID for any TRANSACTION_ID.
Resubmitting an Errored Row:
During Item Interface processing, rows can error out either due to validation (indicated by PROCESS_FLAG = 3 in MTL_SYSTEM_ITEMS_INTERFACE and the corresponding error in MTL_INTERFACE_ERRORS) or due to an Oracle Error.
When an Oracle Error is encountered, the processing is stopped and everything is rolled back to the previous save point. This could be at PROCESS_FLAG = 1, 2, 3, or 4.
When you encounter rows errored out due to validations, you must first fix the row corresponding to the error with the appropriate value. Then reset PROCESS_FLAG = 1, INVENTORY_ITEM_ID = null, and TRANSACTION_ID = null. Then resubmit the row for reprocessing.
Useful Query:
Select
SEGMENT1,
DESCRIPTION,
PROCESS_FLAG,
SET_PROCESS_ID,
INVENTORY_ITEM_ID,
ORGANIZATION_ID,
ORGANIZATION_CODE,
CREATION_DATE,
ITEM_TYPE,
UNIT_OF_ISSUE,
TEMPLATE_ID,
TEMPLATE_NAME,
EXPENSE_ACCOUNT,
ENCUMBRANCE_ACCOUNT,
PRIMARY_UOM_CODE,
PRIMARY_UNIT_OF_MEASURE,
MIN_MINMAX_QUANTITY,
MAX_MINMAX_QUANTITY,
TAX_CODE,
REQUEST_ID
from
MTL_SYSTEM_ITEMS_INTERFACE
order by CREATION_DATE;
----------------------------
Select
ORGANIZATION_ID,
UNIQUE_ID,
REQUEST_ID ,
TABLE_NAME ,
COLUMN_NAME,
ERROR_MESSAGE
CREATION_DATE,
MESSAGE_TYPE
from
MTL_INTERFACE_ERRORS
order by CREATION_DATE;
Useful Metalink Note:
- FAQ for Item Import [ID 109628.1]
- Error in Validating MTL_SYSTEM_ITEMS_INTERFACE [ID 1057175.6]
- A Guideline to IOI Error Messages and Solutions [ID 52746.1]
- How to Import Item Costs Using the Item Open Interface (IOI) [ID 191376.1]
- Item Import Performance Tips [ID 66496.1]
- INCOIN: Basic Steps for Researching Failed Item Imports [ID 552683.1]
- Troubleshooting Guide for INV_IOI_MASTER_CHILD Errors in Item Import [ID 429924.1]
- How To Prepare to Run Parallel Runs of the Item Import Interface INCOIN [ID 842767.1]
- Item Import Gives Error: “The Default Primary Unit of Measure Is Invalid” [ID 789927.1]
- Understanding Item Import and Debugging Problems with Item Import [ID 268968.1]
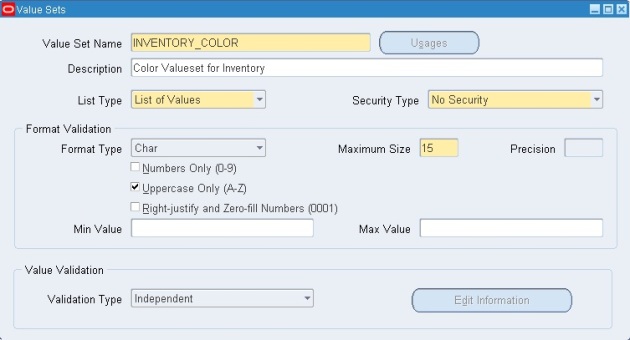
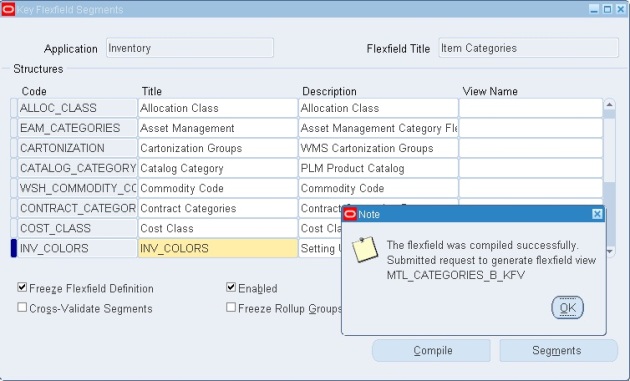
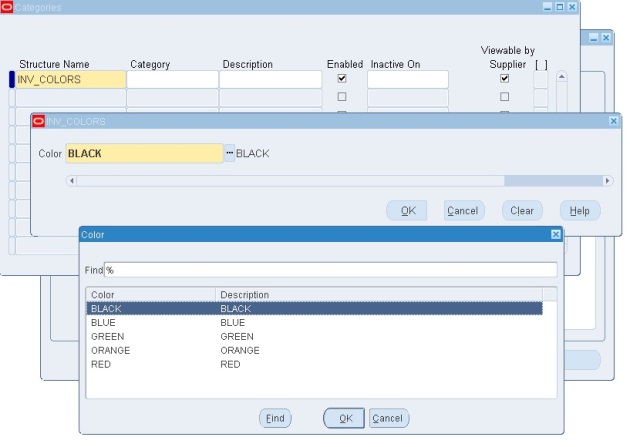
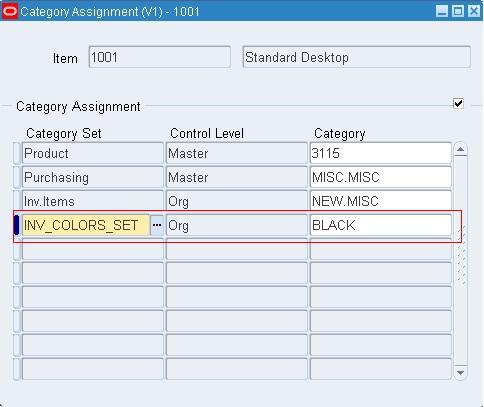
- How to create a Category Set and Assign Items to Categories [ID 423551.1]
- Item API Or Concurrent Manager, Which One Is Best For Item Creation? [ID 760498.1]